Navigating Large Legacy Codebases Navigating Large Legacy Codebases
|
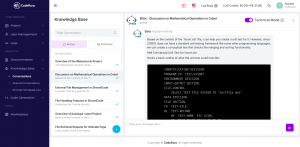
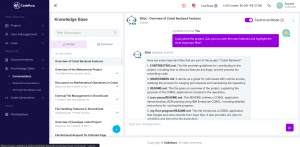
- Instantly surfaces business-critical logic from sprawling COBOL, FORTRAN, or RPG systems with intelligent code mapping.
- Identifies cross-program dependencies, data flows, and integration points that would otherwise take weeks to uncover manually.
- Highlights undocumented or risky components (e.g., hard-coded rules, manual overrides) to prioritize modernization efforts.
|
 Accelerating Onboarding in Legacy Environments Accelerating Onboarding in Legacy Environments
|
- Provides contextual explanations of legacy modules and subsystems, reducing ramp-up time for new team members.
- Enables junior developers to ask natural-language questions (“What does this COBOL subroutine do?”) and get reliable answers.
- Acts as a persistent team memory—no need to rely on tribal knowledge or hunt through outdated documentation.
|
 Reducing Key-Person Dependency in Legacy Systems Reducing Key-Person Dependency in Legacy Systems
|
- Codifies decades of system knowledge from retiring engineers by generating AI-driven documentation and system maps.
- Offers self-service support for internal teams who would otherwise depend on a handful of SMEs.
- Supports cross-training by letting broader engineering teams safely explore and understand legacy logic.
|
 Enhancing Knowledge Transfer During Modernization Enhancing Knowledge Transfer During Modernization
|
- Automatically annotates legacy code with human-readable insights to make transition planning easier.
- Summarizes program flows, data models, and architectural patterns to support replatforming or refactoring initiatives.
- Integrates with Slack, GitHub, or JIRA to deliver modernization insights where teams already work.
|
 Streamlining Legacy Project Oversight for Non-Technical Leaders Streamlining Legacy Project Oversight for Non-Technical Leaders
|
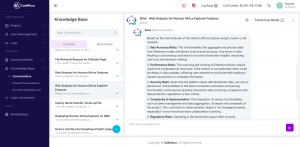
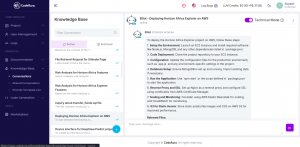
- Translates technical debt, system bottlenecks, and API limitations into clear business language.
- Helps PMs, analysts, and compliance leads understand where modernization risk—and opportunity—exists.
- Enables stakeholders to ask strategic questions (“Which legacy components affect our FedNow readiness?”) and get actionable answers.
|
 Optimizing Developer Allocation in Modernization Projects Optimizing Developer Allocation in Modernization Projects
|
- Reduces manual analysis time by identifying low-risk modules suitable for automated refactoring.
- Prioritizes modernization tasks based on business impact and technical complexity.
- Allows senior engineers to focus on architecture decisions, while AI handles legacy reverse engineering and documentation.
|